John Deere error codes are a vital diagnostic tool, providing insight into the health and performance of various components within the machinery (tractors, loaders, combines & other agriculture equipment). These codes are generated by onboard computer systems, which monitor everything from engine performance to hydraulic systems, transmission functions, electrical circuits, and more.

Understanding John Deere DTC codes is essential for technicians and operators alike. They serve as a roadmap to identify issues swiftly, enabling timely maintenance or repairs to minimize downtime and optimize productivity. In this guide, we’ll delve into the intricacies of John Deere error codes, exploring their classification, and interpretation.

Whether you’re a seasoned technician or a newcomer to the world of heavy machinery, this guide aims to empower you with the knowledge needed to tackle errors effectively and keep John Deere equipment operating at peak performance.
John Deere Error Code Types
Categorizing John Deere error codes into groups can help users quickly identify the type of issue they are dealing with, facilitating more efficient troubleshooting and repair processes.
| Controller | Description |
|---|---|
| ACU | Armrest Controller Unit (ACU error codes 000158.04 – 524254.31) |
| AIC | Armrest Interface Control Unit (AIC error codes 000158.03 – 524224.09) |
| ATC | Automatic Temperature Control (ATC error codes 000168.03 – 600006.13) |
| ASU | Active Seat Control Unit |
| BRC | Front Brake Control Unit |
| BCU | Controls Basic Functions of the Tractor & Rear Hitch |
| BIF | Basic Informator Controls Display, Indicators, & Instruments |
| CAB | John Deere CAB Control Unit |
| CCU | Chassis Control Unit Controls Various Functions |
| CLC | Cab Load Center Control Unit |
| CRU | Controls Functions of the Radio |
| CSC | Controls the Cab Suspension |
| CSM | Cabin Switch Module |
| DSM | Responsible for the Keyboard of the DTI |
| DTI | CommandCenter™ Allows Various Adjustments and Data Retrieval |
| ECU | John Deere Engine Control Unit |
| EPC | Controller for PowrQuad™ Plus and AutoQuad Transmissions |
| ETC | Controller for the Heater & Air Conditioning System |
| FCC | Controls Wipers & Processes Signals |
| GPM | Control Software for Activation of Gear Solenoids |
| HCC | Hitch Control Unit |
| HTC | Controller for the Heater |
| HV1 | Hitch Valve Control Unit |
| ICC | Instrument Cluster Control |
| JDL | JDLink™ Integrated Telematics System |
| OIC | Receives Signals From Relevant Operating Controls |
| PAP | Controls Solenoids for PTO Speed |
| PDU | Primary Display Unit |
| PLC | Electronic Park Lock With AutoPowr™/IVT Transmission |
| PL1 – PL4 | Control Software for Activation of Park Lock Solenoid |
| PTA | Controls Transmission on Vehicles With AutoPowr/IVT |
| PTD | Control Software for Activation of Proportional Solenoids |
| PTF | Controls the Front PTO |
| PTH | Power Train Hydrostatic Control Unit |
| PTI | Power Train Control Unit |
| PTP | PowerShift™ Transmission Control Unit |
| PTQ | Controls Transmission on Vehicles With PowrQuad™ |
| PTR | Power Train Reverser |
| RLC | Controls Lights in the Roof, Cab Frame, Rear Window |
| RPM | Control Software for Activation of Range Solenoids |
| RPT | Controls the Rear PTO |
| SCC | Selective Control Valve CAN Control Unit |
| SCO | Controls the E-SCV Selective Control Valves |
| SFA | Suspended Front Axle Control Unit |
| SIC | Control Unit for the ESCVs/EICVs |
| SSU | Controller for AutoTrac™ Automatic Steering System |
| SV1 – SV7 | Selective Control Valve Unit |
| TCU | Control Unit for AutoPowr™/IVT Transmission |
| TEC | Interface for Tractor Equipment |
| TEI | Tractor Electronic Interface |
| TIA | Controls Transmission on Vehicles With AutoPowr™/IVT |
| TID | Activation of the Transmission Enable Function |
| TIQ | Transmits to the PTQ Control Software |
| TSC | Controls Functions for Front Wheel Drive Axle & Suspension |
| UIC | Transmission Control With AutoPowr™/IVT |
| UIM | Responsible for the Keyboard of the GreenStar™ Display |
| VLC | Vehicle Load Center Control Unit |
| VTV | Controls the CommandCenter™ Display |
| VTI | Controls the GreenStar™ Display |
| XMC / XSC | Controls the AutoTrac™ Automatic Steering System |
Common John Deere Tractor Problems
Common problems with John Deere tractors can vary depending on the specific model, age, and usage. However, some issues tend to occur more frequently across different models. Here are a few common problems that owners may encounter with John Deere tractors:
- Engine Issues: Engine problems can include issues with starting, loss of power, rough idling, or excessive smoke from the exhaust. These issues can stem from fuel system problems, air intake issues, ignition system faults, or engine wear and tear.
- Electrical Problems: Electrical issues such as dead batteries, faulty wiring, blown fuses, or malfunctioning switches and sensors can cause various problems with the tractor’s electrical systems, including lighting, starting, and monitoring functions.
- Hydraulic System Failures: Hydraulic system failures can manifest as slow or erratic hydraulic operation, leaks, or loss of hydraulic pressure. Common causes include worn seals, damaged hoses, or problems with the hydraulic pump or control valves.
- Transmission Problems: Transmission issues may include difficulty shifting gears, slipping gears, or unusual noises during operation. Problems can arise from low transmission fluid levels, worn clutch components, or internal transmission damage.
- Steering and Suspension Troubles: Steering problems such as difficulty turning, excessive play, or uneven steering can be caused by issues with the steering gearbox, linkage, or power steering system. Suspension problems may include worn or damaged components, resulting in a rough ride or instability.
- Brake System Malfunctions: Brake system problems may include ineffective braking, brake dragging, or brake pedal sinking. Issues can stem from worn brake pads, damaged brake lines, air in the brake system, or faulty brake components.
- Cooling System Issues: Cooling system problems such as overheating or coolant leaks can lead to engine damage if not addressed promptly. Common causes include coolant leaks, clogged radiators, malfunctioning water pumps, or faulty thermostats.
- PTO (Power Take-Off) Problems: PTO issues may include failure to engage or disengage, unusual noises, or reduced PTO output. Problems can arise from worn PTO clutches, damaged PTO shafts, or hydraulic system issues affecting PTO operation.
Regular maintenance, timely repairs, and proper operation can help prevent and mitigate these common problems with John Deere tractors. Additionally, consulting the tractor’s user manual and seeking assistance from authorized John Deere service technicians can help diagnose and address specific issues effectively.
Common John Deere Engine Problems
While John Deere engines are known for their durability and reliability, they can still experience problems over time due to various factors. Here are some common engine issues that John Deere owners may encounter:
- Starting Problems: Difficulty starting the engine, especially when cold, can be caused by issues such as a weak battery, faulty starter motor, worn ignition components, or fuel system problems like air in the fuel lines or a clogged fuel filter.
- Loss of Power: Loss of engine power during operation can result from various issues, including fuel delivery problems (e.g., clogged fuel injectors, fuel pump failure), air intake restrictions (e.g., dirty air filter), ignition system faults (e.g., faulty spark plugs, ignition coil issues), or internal engine wear and tear.
- Overheating: Engine overheating can occur due to insufficient coolant levels, coolant leaks, a malfunctioning thermostat, a clogged radiator, a failing water pump, or inadequate airflow to the radiator (e.g., clogged radiator fins, malfunctioning cooling fan).
- Excessive Smoke: Excessive smoke from the exhaust can indicate different engine issues depending on the color of the smoke:
- Black Smoke: Indicates fuel-related problems such as over-fueling, incomplete combustion, or a malfunctioning fuel injector.
- Blue Smoke: Suggests oil-related issues such as worn piston rings, valve seals, or cylinder walls, leading to oil burning in the combustion chamber.
- White Smoke: Indicates coolant entering the combustion chamber due to a blown head gasket, cracked cylinder head, or other cooling system problems.
- Rough Idling: Rough idling, characterized by uneven engine speed or vibration at idle, can be caused by issues such as dirty or clogged fuel injectors, ignition system problems (e.g., faulty spark plugs, ignition coil issues), vacuum leaks, or engine timing issues.
- Oil Leaks: Oil leaks can occur from various engine components such as the valve cover gasket, oil pan gasket, oil filter housing, or seals. Common causes include worn gaskets, loose fasteners, or damaged seals.
- Engine Knocking or Ticking: Engine knocking or ticking noises may indicate issues such as worn engine bearings, piston slap, valve train problems, or low oil pressure. Ignoring these noises can lead to severe engine damage if not addressed promptly.
- Fuel System Problems: Fuel system issues such as contaminated fuel, fuel pump failure, clogged fuel filters, or air in the fuel system can cause engine performance problems, including rough running, stalling, or difficulty starting.
Regular maintenance, including oil and filter changes, coolant system checks, fuel system inspections, and addressing issues promptly, can help prevent and mitigate common engine problems in John Deere equipment. Additionally, following the manufacturer’s recommended maintenance schedule and using genuine John Deere replacement parts can contribute to engine longevity and performance.
How to Read John Deere Error Codes?
Reading John Deere error codes requires accessing the diagnostic system of the specific equipment or vehicle. Here’s a general guide on how to read John Deere error codes:
- Identify the Diagnostic System: John Deere equipment is equipped with onboard diagnostic systems that monitor various components and systems for faults or malfunctions. These diagnostic systems may vary depending on the model and type of equipment.
- Access the Diagnostic Interface: To read error codes, you typically need to access the diagnostic interface of the equipment. This interface may be accessed through a display screen, onboard computer, or diagnostic tool provided by John Deere.
- Navigate to the Error Code Menu: Once you access the diagnostic interface, navigate to the menu or section that displays error codes. This menu may be labeled as “Fault Codes,” “Diagnostic Trouble Codes (DTCs),” or something similar.
- View the Error Codes: In the error code menu, you’ll see a list of alphanumeric codes along with brief descriptions of the associated faults or malfunctions. Each error code corresponds to a specific issue detected by the diagnostic system.
- Interpret the Error Codes: Error codes typically consist of a combination of letters and numbers. The letters often indicate the system or component affected by the fault, while the numbers provide further details about the specific issue. For example:
- “ECU” may indicate an issue with the engine control unit.
- “PTO” may indicate a problem with the power take-off system.
- “EPC” may indicate an issue with the transmission control unit.
- Refer to the Manual or Guide: To understand the meaning of each error code in detail, refer to the equipment’s operator’s manual, service manual, or diagnostic code guide provided by John Deere. These resources contain comprehensive lists of error codes along with explanations and troubleshooting steps.
- Address the Issues: Once you’ve identified the error codes and understood their meanings, you can take appropriate action to address the underlying issues. This may involve inspecting and troubleshooting the affected components, performing repairs or adjustments, or seeking assistance from a qualified technician or dealer.
- Clearing Error Codes (Optional): After addressing the issues and making necessary repairs, you may have the option to clear the error codes from the diagnostic system. This step is usually performed through the diagnostic interface or by following specific procedures outlined in the equipment’s manual.
It’s essential to follow proper safety procedures and guidelines when troubleshooting or working on John Deere equipment, especially when dealing with diagnostic systems and electrical components. If you’re unsure about interpreting error codes or performing repairs, consult the equipment’s manual or seek assistance from a certified John Deere dealer or service technician.
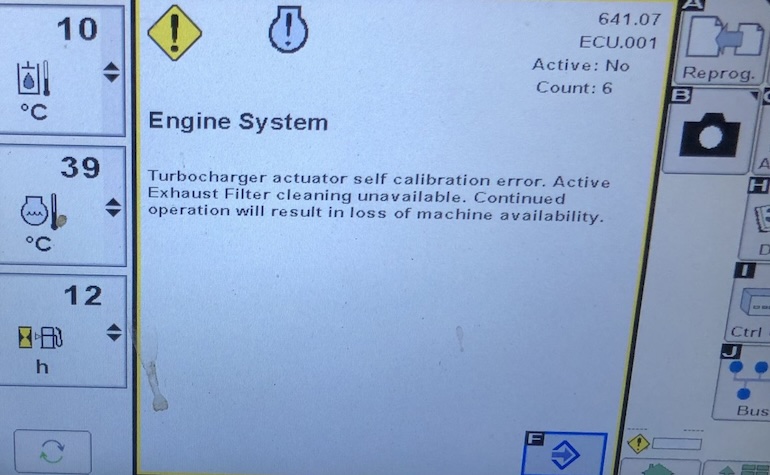
Sample: John Deere Error Code ECU 000641.07 (ECU 641.07)
The Variable Geometry Turbo Actuator Position Sensor Issue
ECU 000641.07 – The Variable Geometry Turbo Actuator Position Sensor Issue
Turbocharger actuator self calibration error. Active Exhaust Filter cleaning unavailable. Continued operation will result in loss of machine availability.





