- On-Road Vehicle Emission Standards
- US EPA (Environmental Protection Agency)
- US CARB (California Air Resources Board)
- EURO (European Emission Standards)
- Japan – J-LEV Regulations
- Non-Road (Off-Highway) Standards
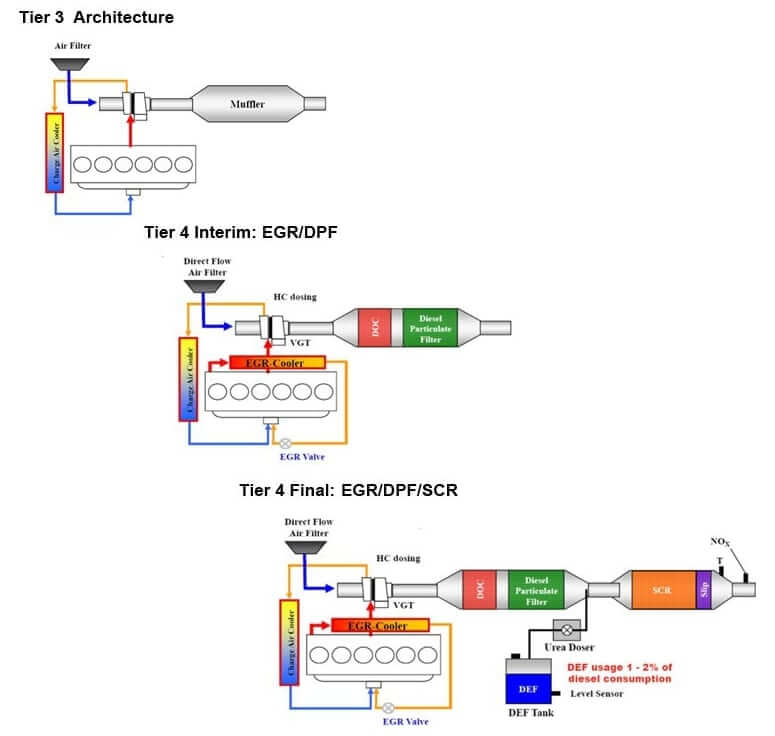
- United States – EPA Tier Standards
- Europe – Stage I to Stage V (Non-Road Mobile Machinery)
- China – NR (Non-Road) Emission Standards
- India – Bharat (CEV/TREM) Stage II to Stage V
- IMO (International Maritime Organization)
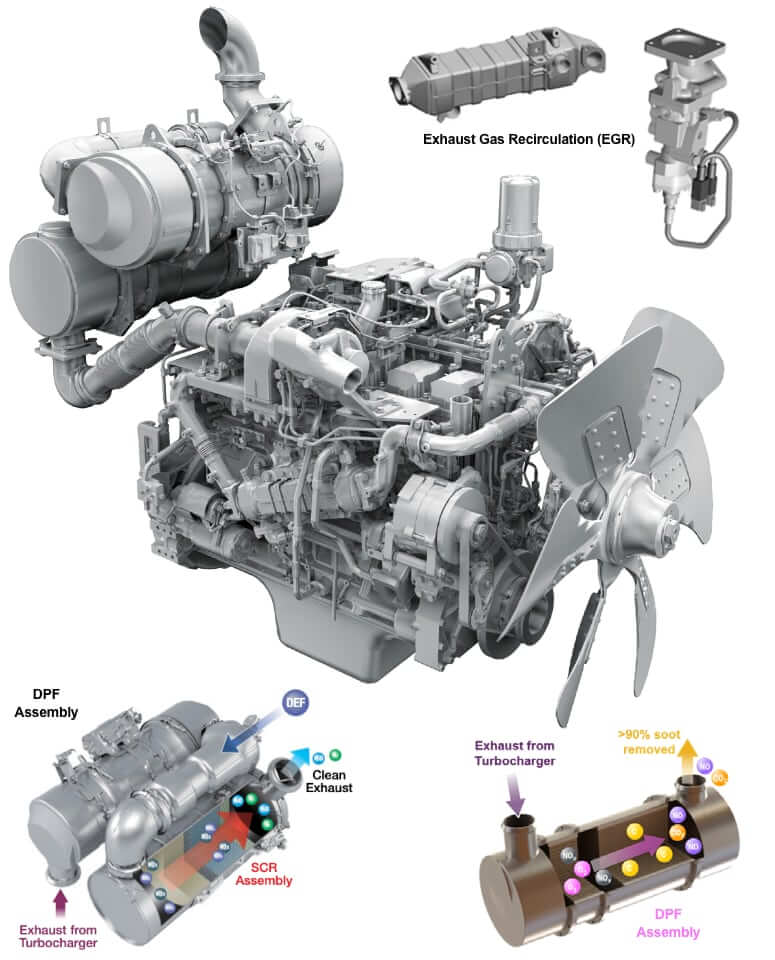
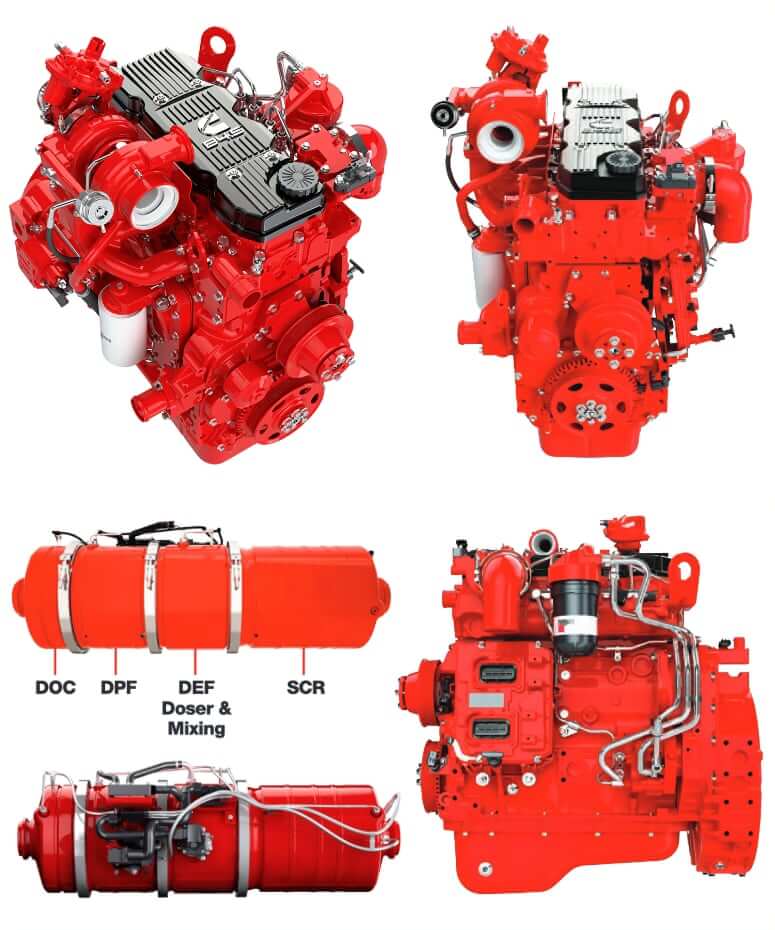
- Engine Emission Control Abbreviations
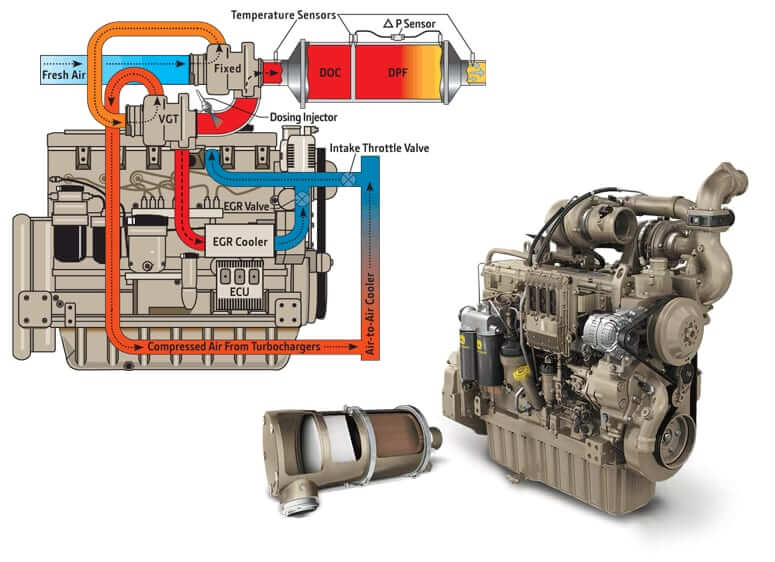
- DOC (Diesel Oxidation Catalyst)
- DPF (Diesel Particulate Filter)
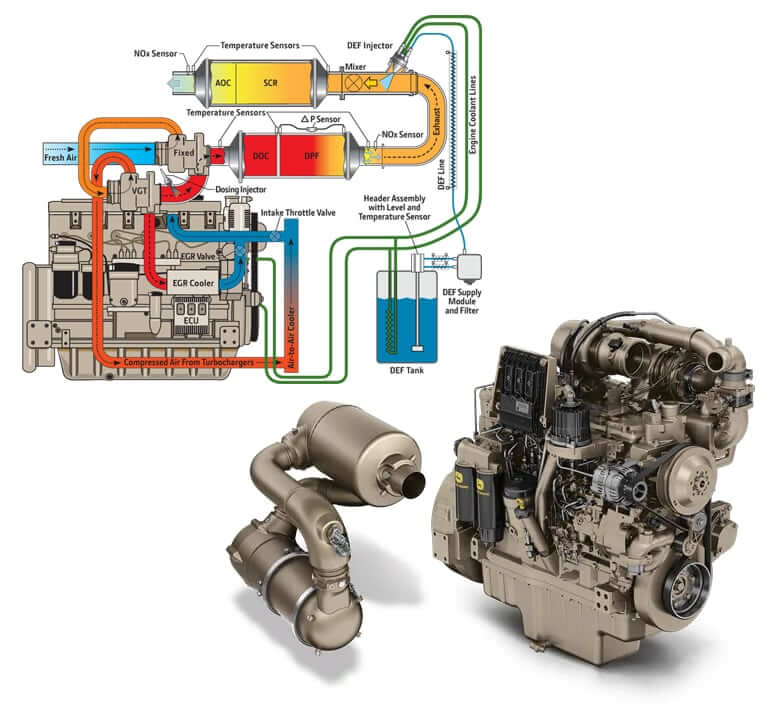
- SCR (Selective Catalytic Reduction)
- EGR (Exhaust Gas Recirculation)
- DEF (Diesel Exhaust Fluid)
- CCV (Closed Crankcase Ventilation)
- Emission Standards Comparison
- Emission Standards Comparison Chart (Tier 4 Final vs Stage V)
- Non-Road Diesel Engine Emission Standards Comparison
- US EPA Tier 4F vs EU Stage V (Key Differences)
To reduce the environmental and health impacts of diesel engines used in vehicles and off-road equipment, international emission standards focus on limiting the release of several key pollutants. These pollutants are the primary contributors to air quality degradation and are closely monitored across various regulatory systems, including EPA Tier (USA), EU Stage (Europe), China NR, and India Bharat CEV standards.
Advanced emissions control technologies – such as Diesel Particulate Filters (DPF), Selective Catalytic Reduction (SCR), and Exhaust Gas Recirculation (EGR) – are employed to meet these stringent regulations.

The four main pollutants typically regulated are:
- Particulate Matter (PM) – fine particles that can penetrate deep into the lungs, causing respiratory and cardiovascular issues.
- Nitrogen Oxides (NOx) – a major cause of smog and acid rain; also linked to respiratory problems.
- Carbon Monoxide (CO) – a colorless, odorless gas that is toxic in high concentrations.
- Hydrocarbons (HC) – unburned fuel emissions that contribute to ozone formation and smog.
By limiting these emissions, regulatory bodies worldwide aim to ensure cleaner air, improved public health, and a sustainable future for construction, agriculture, transportation, and industry.
On-Road Vehicle Emission Standards
International Emission Standards are regulations that limit the amount of pollutants (like NOx, CO, HC, PM) emitted by vehicles and non-road machinery, including construction equipment. These standards aim to reduce air pollution and promote cleaner technologies globally.
US EPA (Environmental Protection Agency)
- Definition: U.S. agency that regulates emissions from engines and vehicles.
- Standards: Current on-road standard: EPA 2027/Phase 3 (proposed for heavy-duty)
- Purpose: Reduces emissions of nitrogen oxides (NOx), hydrocarbons (HC), particulate matter (PM), and carbon monoxide (CO).
US CARB (California Air Resources Board)
- Definition: State-level agency setting stricter emissions standards in California.
- Standards: Low-Emission Vehicle (LEV), Ultra-Low Emission Vehicle (ULEV), and Zero Emission Vehicle (ZEV).
- Purpose: Reduces vehicle emissions beyond federal EPA standards.
EURO (European Emission Standards)
- Definition: EU regulations governing emissions from engines in road vehicles. Gets progressively stricter from Euro 1 (1992) to Euro 6 (2014+)
- Standards: EURO 1 to EURO 7 for on-road vehicles. Currently up to Euro 6d for light-duty and Euro VI-E for heavy-duty vehicles.
- Purpose: Limits emissions of NOx, PM, HC, and CO.
Japan – J-LEV Regulations
- Equivalent to Euro 6 or stricter in some segments
- Japan has independent standards for domestic and imported vehicles
Non-Road (Off-Highway) Standards
These apply to agricultural, forestry, and construction machinery like tractors, loaders, excavators, bulldozers, etc.
United States – EPA Tier Standards
- Tier 1 to Tier 4 Final for heavy equipment
- Tier 4 Final (2014+) requires major reductions in PM and NOx using advanced technologies
Europe – Stage I to Stage V (Non-Road Mobile Machinery)
- Stage V is the current most stringent standard (from 2019–2021 depending on power category)
- Covers engines from 0–560 kW
- Introduced a particle number (PN) limit in addition to PM mass
China – NR (Non-Road) Emission Standards
- China NR III to NR IV and NR V
- Largely harmonized with European standards
India – Bharat (CEV/TREM) Stage II to Stage V
- Bharat Stage IV/V for construction equipment (aligned with Euro IV/V)
IMO (International Maritime Organization)
As of 1 January 2020, new emission standards are enforced for fuel oil used by ships, in a regulation known as IMO 2020. The global sulphur limit (outside SECA’s) dropped from an allowed 3.5% sulphur in marine fuels to 0.5%. Sets emission regulations for marine engines. Reduces NOx, SOx, and PM emissions from ships.
- IMO Tier I, II, and III

Engine Emission Control Abbreviations
These abbreviations and definitions outline how global emission standards aim to reduce air pollution from engines, enhancing air quality and environmental protection.
DOC (Diesel Oxidation Catalyst)
- Definition: A device that converts hydrocarbons (HC) and carbon monoxide (CO) into carbon dioxide (CO₂) and water (H₂O).
- Purpose: Reduces HC and CO emissions.
DPF (Diesel Particulate Filter)
- Definition: Captures and removes particulate matter (PM) from exhaust gases.
- Purpose: Reduces soot emissions.
SCR (Selective Catalytic Reduction)
- Definition: Uses diesel exhaust fluid (DEF) to reduce NOx emissions.
- Purpose: Converts NOx to nitrogen (N₂) and water vapor.
EGR (Exhaust Gas Recirculation)
- Definition: Recirculates exhaust gases back into the engine intake to reduce NOx formation.
- Purpose: Lowers combustion temperatures and NOx emissions.
DEF (Diesel Exhaust Fluid)
- Definition: A urea-based solution used in SCR systems.
- Purpose: Reduces NOx emissions in diesel engines.
CCV (Closed Crankcase Ventilation)
- Definition: Prevents crankcase emissions from being released into the atmosphere.
- Purpose: Reduces HC and PM emissions.
Emission Standards Comparison
Comparison chart of international emission standards for non-road (off-road) construction and agricultural equipment, focusing on EPA Tier 4 Final (USA) vs EU Stage V (Europe).
These are the most widely recognized and enforced standards globally:
Emission Standards Comparison Chart (Tier 4 Final vs Stage V)
| Engine Power Range (kW) | EPA Tier 4 Final (USA) | EU Stage V (Europe) |
|---|---|---|
| 0 – 19 kW | Tier 4 Final (PM + NOx control, no DPF required) | Stage V (DPF required, PN limits apply) |
| 19 – 56 kW | Tier 4 Final (DOC or DPF; SCR not required) | Stage V (DPF + PN limits + SCR or EGR) |
| 56 – 130 kW | Tier 4 Final (SCR + DOC; no PN requirement) | Stage V (SCR + DPF + PN limit mandatory) |
| 130 – 560 kW | Tier 4 Final (SCR + DOC, DPF optional) | Stage V (SCR + DPF + stricter PN limits) |
| >560 kW | Not regulated (or Tier 2/3) in many cases | Stage V (SCR + DPF + PN required for all engines) |
- 0–19 kW – Compact tractors, small tillers, mini dumpers
- 19–56 kW – Small skid steers, mini excavators, utility tractors
- 56–130 kW – Medium tractors, telehandlers, backhoe loaders
- 130–560 kW – Bulldozers, large excavators, combines, large wheel loaders
- >560 kW – Mining haul trucks, industrial generators, special forestry equipment
Non-Road Diesel Engine Emission Standards Comparison
Comparison chart of major international emission standards for non-road diesel engines (e.g., construction & agricultural equipment) focusing on PM and NOx levels – the two most critical pollutants.
| Power Range (kW) | US EPA Tier 4 Final | EU Stage V | China NR IV |
|---|---|---|---|
| 0 – 8 kW | Not regulated | PM: 0.6 / NOx: 7.5 | PM: 0.6 / NOx: 7.5 |
| 8 – 19 kW | PM: 0.6 / NOx: 7.5 | PM: 0.6 / NOx: 7.5 | PM: 0.6 / NOx: 7.5 |
| 19 – 37 kW | PM: 0.03 / NOx: 4.7 | PM: 0.015 / NOx: 0.4 + PN limit | PM: 0.03 / NOx: 4.7 |
| 37 – 56 kW | PM: 0.02 / NOx: 0.4 | PM: 0.015 / NOx: 0.4 + PN limit | PM: 0.02 / NOx: 0.4 |
| 56 – 130 kW | PM: 0.02 / NOx: 0.4 | PM: 0.015 / NOx: 0.4 + PN limit | PM: 0.02 / NOx: 0.4 |
| 130 – 560 kW | PM: 0.02 / NOx: 0.4 | PM: 0.015 / NOx: 0.4 + PN limit | PM: 0.02 / NOx: 0.4 |
| >560 kW | PM: 0.04 / NOx: 0.67 | PM: 0.015 / NOx: 0.67 + PN limit | PM: 0.04 / NOx: 0.67 |
Note:
- PM = Particulate Matter (g/kWh)
- NOx = Nitrogen Oxides (g/kWh)
- PN = Particle Number (Stage V only, limits particle count in addition to weight)
US EPA Tier 4F vs EU Stage V (Key Differences)
| Feature | EPA Tier 4 Final | EU Stage V |
|---|---|---|
| Applies to all engines | Yes | Yes |
| PM limit | 0.02 g/kWh | 0.015 g/kWh |
| Particle Number (PN) Limit | ❌ Not applied | ✅ Applied for 19–560 kW |
| Retrofit requirement | ❌ No | ✅ Yes, for many urban zones |
| Certification | US EPA Certificate | EU Type-approval (Reg. 2016/1628) |
| DEF / SCR required | ✅ Often | ✅ Often |
| DPF required | ✅ Yes (for PM control) | ✅ Yes (to meet PN limits) |
International emission standards play a critical role in shaping the future of cleaner, more efficient engines for both on-road vehicles and off-road equipment. From EPA Tier 4 Final in the U.S. to EU Stage V in Europe, and emerging standards in countries like China and India, these regulations are driving innovation in engine design and aftertreatment technologies.
As governments tighten emission limits to combat air pollution, manufacturers are responding with advanced systems like DPF, SCR, EGR, and electronic engine controls. The result is a new generation of machinery that delivers better fuel efficiency, reduced environmental impact, and improved operator safety.
For equipment owners, operators, and fleet managers, understanding these standards isn’t just a regulatory requirement – it’s essential for choosing compliant machines, maintaining uptime, and ensuring long-term sustainability in a rapidly evolving global market.






What do engine emission standards such as CARB T3 NR and China II NRNC mean?
CARB T3 NR = California Air Resources Board U S EPA Tier 3 NR Nonroad Equivalent (Not Currently EPA Certified)
China II NRNC = China Stage II Nonroad and Non-Certified
How to read these abbreviations – EPA T4F NRNG?
US EPA Tier 4 Final Nonroad Non-Genset Equivalent (Certified to U.S. EPA & California ARB Tier 4 Final Nonroad Non-Genset Standards)